When I began the journey of learning more about SEO, finding a simplified technical SEO roadmap proved challenging. I had to spend more time scanning through different articles which to a larger extent were good and authoritative.
However, they did not share information in a more simplified manner which could help one transition from a beginner to an expert. In this article, I will hold your hand and guide you through a step-by-step process of learning all you need to know about technical SEO.
If this sounds interesting to you then you are in the right place. Just continue reading.
This guide discusses:
- Chapter One: Technical SEO (Definition & Importance)
- Chapter Two: Key Elements of Technical SEO
- Chapter Three: Crawling and Indexing
- Chapter Four: Page Speed
- Chapter Five: Duplicate and Thin Content
- Chapter Six: Additional Technical SEO Techniques
- Final Thoughts
Chapter One: Technical SEO (Definition & Importance)
Definition
Technical SEO refers to a set of website and server optimization practices aimed at helping search engines crawl your website based on specific factors such as speed, responsiveness, quality of content, site structure, and sitemap.
In simple terms, technical SEO ensures that your website can be identified, crawled, and ranked by Google and other search engines.
You should know that search engines such as Google prefer websites that uphold their webmaster guidelines.
Consequently, your website content should be accurate, accessible, and user-friendly.
Importance of Technical SEO

Imagine having the best content on your website with important and exciting information that makes it a ‘must-read’ for your target audience.
However, when your audience clicks through its link, the article takes time (more than 10 seconds) to load. Furthermore, the wording and graphical content of the article appear to be out of place.
Truth be told;
Such content will annoy your readers hence leading to a higher bounce rate.
From a search engine optimization (SEO) perspective, you will not only lose traffic regardless of how great the content was but also experience a drop in SERP (Search Engine Result Page) rankings.
Related Article: How Search Engines Work
This is just one out of the many examples of the importance of technical SEO
You should also know that without a practical and working technical SEO strategy, chances are high that your website wouldn’t be identified, crawled, and indexed by Google and other search engines such as Bing.
Consequently, you will become one of the 90.63% of websites that do not benefit from Google’s organic search traffic.
At this point, I know you might be asking;
“What if my website can be found directly by my customers?”
Simply put;
There are situations where your customers directly visit your website via the website URL/ direct link to the home page.
However, without the implementation of strategic technical SEO practices, chances are high that they will experience other user experience issues such as slow page loading speeds and unresponsive pages that come along with confusing navigation.
Such user experience issues negatively impact your website’s SEO.
Key Elements of Technical SEO
Technical SEO goes beyond crawling and indexing. It encompasses other critical elements such as:
- Site Architecture
- URL structure
- Duplicate Content
- Thin Content
- Canonical Tags
- 404 Pages
- Javascript
- XML Sitemaps
- Structured Content
- Hreflang
Just a reminder, I promised you a technical SEO roadmap earlier on that would help you transition smoothly from a beginner to an expert.
Bearing this in mind, let’s dive into the details.
Chapter Two: Site Architecture (Structure & Navigation)
I believe that site structure is foundational when it comes to technical SEO. To a larger extent, it comes even before the element of crawling and indexing.
Based on my long-term experience in SEO, I am convinced that most crawling and indexing problems originate from poorly designed website structures. In this regard, I insist that you should always get the site structure and navigation step right.
It is also worth noting that site structure guides all the other optimization processes such as the website URLs, robots.txt files, and even the internal linking strategy that you will be using (clusters).
As far as the issues of site structure are concerned, I always recommend the use of Topical Maps.
Topical Maps play a significant role in coming up with an organized site structure such as the one below.
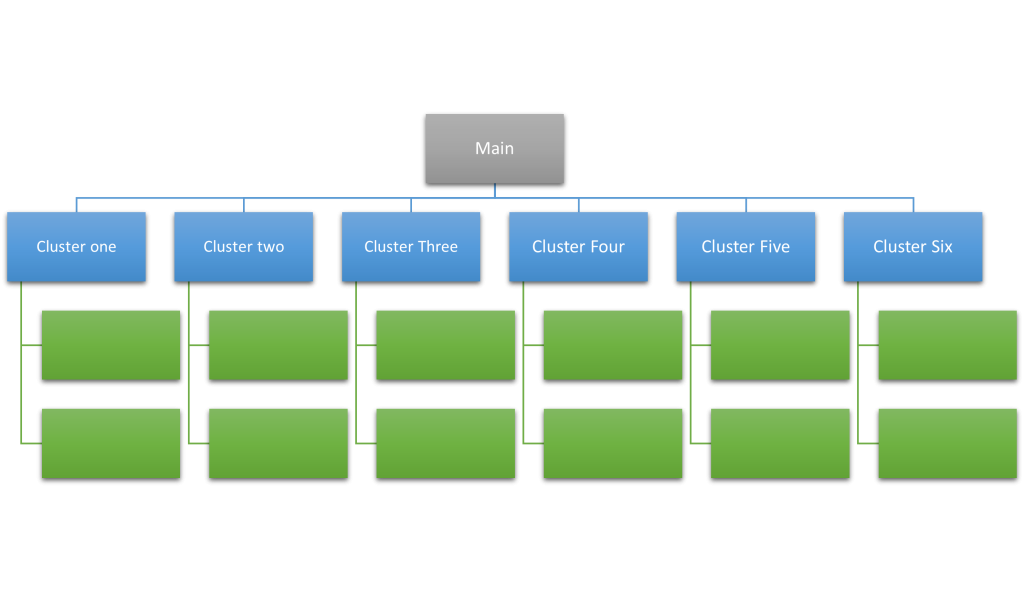
The illustrated structure which also simulates a topical map will make it easier for search engines such as Google to crawl all of your website pages.
Please Note;
Adopting a flat structure or using a topical map should always apply even for e-commerce websites.
URL Structure
When it comes to URL structure, your URLs should be consistent and be based on a logical structure.
In most instances, the usage of breadcrumbs is advised. This will help users understand where they are on your website.
Here’s a good example of a well-structured URL
The URL structure can also be supported by breadcrumb navigation. Breadcrumbs help in improving user experience especially when it comes to conveniently navigating from one page to another
Most importantly, breadcrumbs automatically include internal links to specific category and sub-category pages hence solidifying your website’s structure.
{insert a snapshot of breadcrump links from jonaniseo website}
It’s also worth noting that Google is currently using the breadcrumb approach in the SERPs.
Chapter Three: Crawling and Indexing
The primary focus of this set of elements with regard to technical SEO is to identify and fix crawl issues as well as make it easier for search engine spiders to navigate to your website’s deep pages.
First Step: Identify Indexing Issues
You need to find pages on your website that have not been crawled by search engine spiders due to potential issues.
This step can be achieved in 3 simple ways
First using screaming Frog crawler
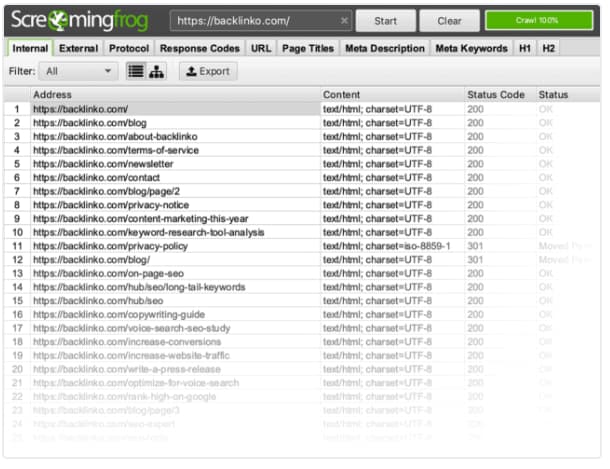
Second, examining the “Coverage Report” in the Google Search Console
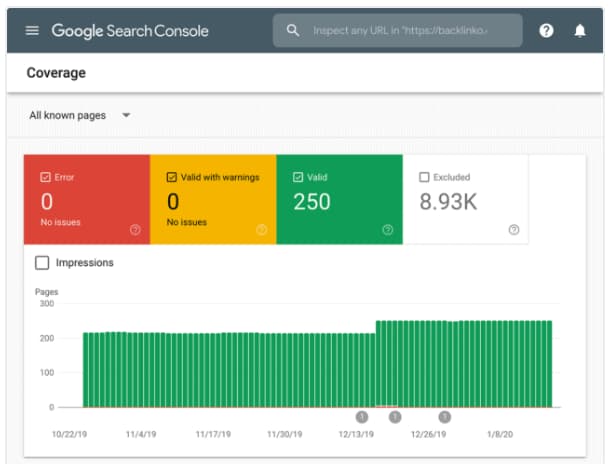
Third conduct an SEO Audit using other SEO tools such as SEMrush
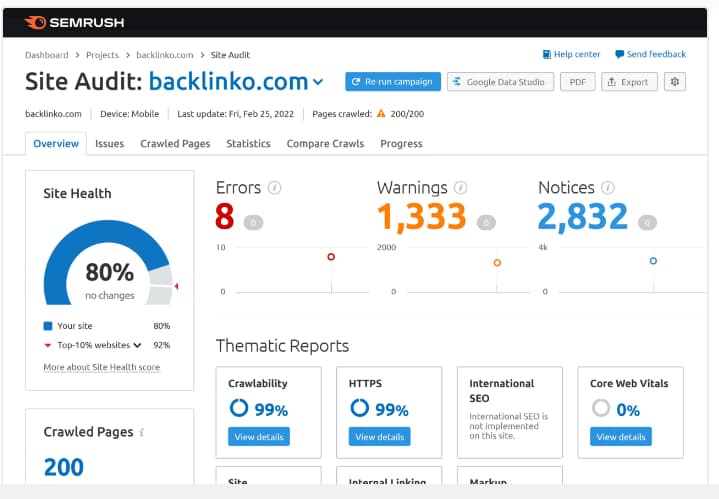
It is worth noting that the highlighted tools have their advantages as well as disadvantages. For this reason, I would recommend that you try out all and any other available tool on most occasions especially when examining a website with at least 90K+ pages.
Second Step: Create Internal Links to Deep Pages
When it comes to the creation of internal links to deep pages, I still insist that having a topical map is crucial.
Why?
A topical map supports the creation of a flat website architecture hence preventing the possibility of unindexed deep pages.
The bottom line is;
A topical map (which supports flat website architecture) brings the “deepest” pages close to the home page through internal linking hence making is easier for search engine spiders to crawl the page.
XML Sitemap
A sitemap is an XML file with a list of important website pages. The primary function of an XML sitemap is to inform search on the pages that your website has and their location.
GSC “Inspect”
This is an important feature in Google’s Search Console that assists in identifying URLs that have not been indexed by Google.
As such, the feature tells you why a page has not been indexed but also provides more information on already indexed pages such as page rendering.
Chapter Four: Page Speed
Page loading speed is integral to amazing user experiences. According to Google, improving your website’s page speed has a direct impact on your site’s rankings.
However, page speed alone cannot guarantee you a place on the first page of Google’s search results.
As such, there are other complementary factors such as backlinks and the authority of your website (E-E-A-T).
Here are 3 simple techniques you can use to boost your website’s loading speed
Technique One: Reduce the Size of Your Web Pages
Conventionally, this technique is achieved by minifying CSS, installing CDN (Content Delivery Network), or using Cache plugins and related configurations.
Based on a study that was conducted by Backlinko, it was discovered that page size correlated with load times.
Here is a snapshot of the study.
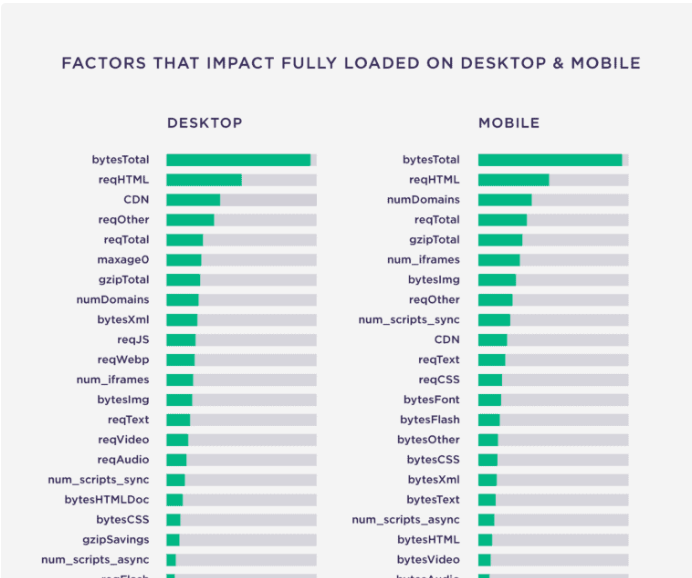
When it comes to using CDNs, please ensure that you have tested the website’s speed with and without the CDN
Technique two: Remove 3rd party scripts
3rd party scripts have adverse effects when it comes to page load time. As such, they increase the page load time.
However, it is important to understand that there are several 3rd party scripts that you might require especially when it comes to running your website effectively. An example of such a script is the one for Google Analytics or Facebook Pixel.
Chapter Five: Duplicate and Thin Content
Duplicate content is a common SEO ranking killer for most websites and most websites fall for this trap.
With the increased accessibility of remote services, you might be tempted to outsource content creation services from either unqualified web content creators or from cheap online avenues.
Either way, both approaches have their pros and cons. However, in most instances, the repercussions exceed the perceived benefits.
Here’s an example;
The content development services might be cheap but they might be associated with generic especially, if content is generated using AI tools. Furthermore, there is a likelihood that the content might be of low quality and duplicated.
The bottom line is;
Cheaper content development services come along with the need for quantity over quality.
As such, the service provider will try to rush and complete more tasks to substantiate target earnings. In the process, AI tools, word spinners, and other easy-to-go strategies will be used hence compromising on the desired quality.
On your side, you will suffer long-term effects such as low-quality, thin, or duplicate content.
Take note that duplicate content can also occur in a situation where your CMS generates several versions of the same page on other URLs.
On the other hand, thin content has adverse effects on your overall website ranking most specifically the SERP results.
How To Fix Duplicate and Thin Content Issues
Option 1: Conduct an SEO Audit to Identify and Correct Duplicate Content
When it comes to SEO Audit, especially for duplicate content, you can use industry tools such as SEMrush and AHrefs.
SEMrush has a “Content Quality” area that helps you establish whether your website has some duplicate content.
Please Note;
Duplicate content can come from your website or other websites.
It is for this reason that you should always check and confirm the uniqueness of your content before uploading it to your website.
You might be asking;
“What if I already have existing published content on my website?”
Here’s the deal;
In such situations, you can use other tools such as Copyscape which comes with the “Batch Search” functionality that allows you to upload multiple URLs and view where the associated content appears around the web.
Another disturbing question might be;
“What if other people copy content from my blog or website and place the content on their sites?”
In this situation, the problem is theirs. Consequently, they are the ones who will suffer related penalties.
Option 2: No-index Critical Pages with Similar Content
When checking for duplicate content, there is a likelihood that you might encounter pages with duplicate content that cannot be changed.
In such situations, it is important to ass the “noindex” tag to the pages
In brief;
The ‘no index’ tag prevents Google and other search engines from indexing assigned page/s
You should know that Google spiders take some time to crawl or re-crawl your website depending on your crawl budget.
Besides using the no-index tag to prevent Google spiders from crawling specific web pages, you can also use the robots.txt file to block the spiders.
Option 3: Canonicalization (Canonical URLs)
Just a quick recap;
If you have been following keenly, I have highlighted so far 2 options for dealing with duplicate content.
Briefly;
I have discussed the usage of an SEO Audit to identify and correct duplicate content. Secondly, I highlighted the use of a no-index tag. As for the third option, I will be discussing the canonicalization technique.
Here’s what you should know;
Canonicalization refers to the process through which Google selects one out of multiple similar pages to index. In this process, the selected URL is referred to as the canonical and will be the one that will show in the search results.
The process of selecting the canonical URL is based on several signals including:
- Duplicate Pages
- Internal Links
- Canonical tags
- Redirects
- Sitemap URLs
Note;
Canonical URLs are a perfect solution for pages with similar content and minor differences.
Let’s take for example an e-commerce website scenario;
In case the website sells t-shirts, there is a likelihood that there might be different links representing different colors, sizes, and material variations of a specific t-shirt.
In such a case,
Canonicalization can be applied in listing the main URL that should be indexed.
It is worth noting that Google’s Indexing process especially when it comes to specific pages can be examined using the URL Inspection tool that is available in Google Search Console.
Chapter Six: Additional Technical SEO Techniques
In the 5 chapters above, the technical SEO roadmap discussed different techniques and concepts relating to technical search engine optimization.
My inspiration for the guide was to come up with something simple and comprehensive.
In addition to what I have discussed above;
Here are other techniques/ tips that might be necessary depending on the insights from your web audit report.
Structured Data
Here’s what you should know about structured data;
First and foremost, it uses specific vocabulary (commonly identified as schema) to categorize while at the same time labeling specific elements on your web pages for Google spiders and other search engine bots.
In simple terms;
I can describe structured data as a vocabulary that reveals to the search engine bot’s elements in your web pages such as products, videos…etc.
Consequently, it helps search engines understand website content.
With all the highlighted information about structured data, the most contentious question in most online platforms and forums is;
“Does setting up Schema directly influence my website SEO?”
The answer is No.
Sounds hard to believe?
Keep reading.
According to a study by Backlinko on a specific set of search engine ranking factors, it was established that there was no correlation between Schema and first-page SERP rankings.
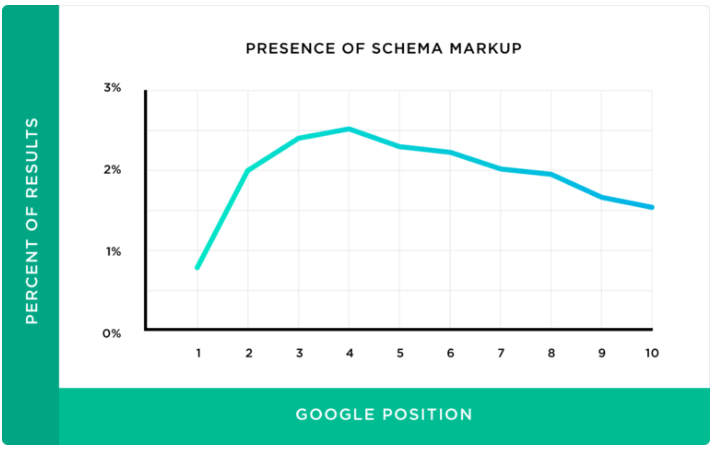
However, you should know that;
The use of Schema can lead to the placement of Rich Snippets on your pages
Since Rich Snippets stand out in the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs), they can immensely improve your website’s organic click-through rate.
Hreflang for Global Sites
In simple terms;
Hreflang refers to an HTML attribute that specifies the language as well as the geographical target of a webpage.
This means that Hreflang can be used in a case whereby your website has multiple versions of the same page but in multiple languages.
In such a situation, Hreflang will reveal the existing variations to Google and other search engines hence making it easier to deliver the specific versions of the pages to the specified users.
Most people who consult me on the placement of Hreflang confess that they experience difficulties setting it up using the Google Guidelines.
But the best part about this technical SEO roadmap guide the process is simplified using a tool.
Here’s a Hreflang Generator tool that can help you address Hreflang issues.
Dead Links Audit
When it comes to dead links, having them on your website is not dangerous to your Search Engine Optimization (SEO) practices.
However, broken internal links are detrimental to your SEO.
Truth is;
They make it difficult for search engines for search engine bots (spiders) to crawl your web pages.
For this reason, always conduct periodical SEO Audits to fix the broken links problem.
Validating XML Site Maps
Websites with a lot of pages come along with the difficulty of keeping track of these pages in their sitemap.
Since the main purpose of a sitemap is to direct search engines to all live pages, it is important to run your sitemap through validation tools such as the “Map Broker XML Site Validator.”
Mobile Usability Audit
Most of your website visitors do it using mobile devices.
You should consistently ensure that your website is super mobile-friendly.
Long story short;
Always review the Google Search Console’s Mobile Usability report to identify and correct some of the web pages that have optimization issues for mobile users.
All Said ….
Remember, SEO is not just a one-time process, problems pop up over time and it’s for this reason that I recommend that you bookmark this technical SEO roadmap guide and check it occasionally to ensure that your website has up-to-date SEO recommendations. Don’t forget to comment, share, and subscribe to our email list for real-time SEO and Google Analytics information and updates.








